概述
本文讨论下Ceph在Jewel中引入的 dynamic throttle:BackoffThrottle;分析后优化Ceph filestore,journal相关的throttle配置;
参考文章:
http://blog.wjin.org/posts/ceph-dynamic-throttle.html
https://fossies.org/linux/ceph/src/doc/dynamic-throttle.txt
BackoffThrottle
Jewel引入了dynamic的throttle,就是代码中BackoffThrottle,现在filestore和Journal都是使用它来做throttle的;
1 | class FileStore |
BackoffThrottle定义和相关参数如下:
1 | /** |
filestore throttle举例分析
下面以使用BackoffThrottle的filestore throttle举例分析下其参数配置
filestore throttle的相关配置项
1 | OPTION(filestore_expected_throughput_bytes, OPT_DOUBLE, 200 << 20) |
根据配置项初始化BackoffThrottle
1 | bool BackoffThrottle::set_params( |
获取delay值
1 | std::chrono::duration<double> BackoffThrottle::_get_delay(uint64_t c) const |
如上述函数描述,分四种情况计算delay值:
- max = 0时:永远返回 0
- current/max < low_threshhold时:返回 0
- low_threshhold <= current/max < high_threshhold时:计算一值
- high_threshhold <= current/max时:计算一值
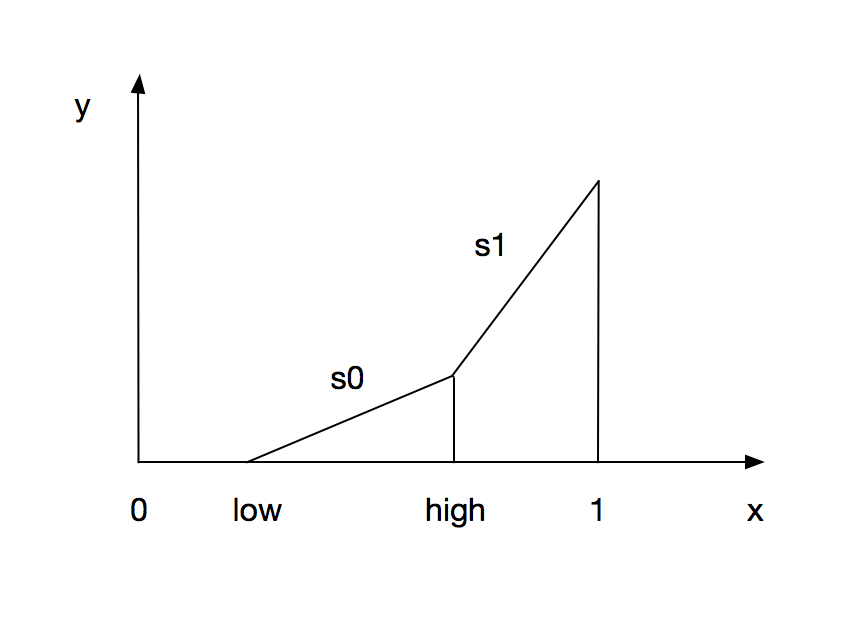
如图所示,在第一个区间的时候,也就是压力不大的情况下,delay值为0,是不需要wait的。当压力增大,x落入第二个区间后,delay值开始起作用,并且逐步增大, 当压力过大的时候,会落入第三个区间,这时候delay值增加明显加快,wait值明显增大,尽量减慢io速度,减缓压力,故而得名dynamic throttle。
默认情况下filestore throttle分析
filestore有bytes和ops两个throttle,这里以bytes为例分析:
默认情况下:
1 | filestore_queue_high_delay_multiple = 0 |
相当于BackoffThrottle中的值如下:
1 | low_threshhold = 0.3 |
所以默认配置下,是关闭dynamic delay的;
开启dynamic throttle
参考最早的代码,配置:
1 | filestore_queue_high_delay_multiple = 2 |
其他使用默认值是,BackoffThrottle中的值如下:
1 | low_threshhold = 0.3 |
则此时的delay分为如下几种:
c:op->bytes,即一次请求的数据量
current:当前filestore queue的数据量,初始化为 0,每次调用:throttle_bytes.get(o->bytes);{ current + = c;}
current/max < low_threshhold时:
此时 current < (30 << 20);delay = 0low_threshhold <= current/max < high_threshhold时:
此时 (30 << 20) <= current < (90 << 20)
delay = c ((current/max - 0.3) s0)
a)current = 30 << 20时:delay = 0
b)current = 90 << 20时:delay = c / (100 << 20)high_threshhold <= current/max时:
此时 (90 << 20) < current
delay = c (2/(200 << 20) + (current/max - 0.9) s1)
a)current = 90 << 20时:delay = c / (100 << 20)
b)current = 100 << 20时:delay = 5 * c / (100 << 20)
当前配置下的dynamic throttle
配置如下:
1 | filestore_expected_throughput_bytes = 536870912 // 512M |
BackoffThrottle中的值如下:
1 | low_threshhold = 0.6 |
则此时的delay分为如下几种:
current/max < low_threshhold时:此时 current < (600 << 20);delay = 0
low_threshhold <= current/max < high_threshhold时:
此时 (600 << 20) <= current < (900 << 20)
delay = c ((current/max - 0.6) s0)
a)current = 600 << 20时:delay = 0
b)current = 900 << 20时:delay = c / (256 << 20)high_threshhold <= current/max时:
此时 (900 << 20) < current
delay = c (2/(512 << 20) + (current/max - 0.9) s1)
a)current = 900 << 20时:delay = c / (256 << 20)
b)current = 1000 << 20时:delay = 5 * c / (256 << 20)
结论:这里的参数配置不是很合理;600M之前的delay都是0;后续随着current的增大,delay的值小于默认时候的值,可能会加大filestore的压力;

